Gastrik Baloon
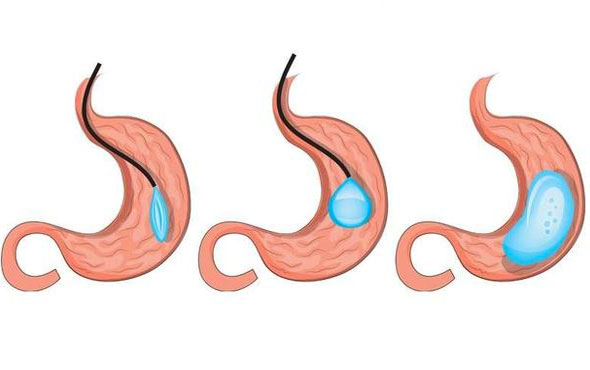
he simplest method to help lose weight is gastric balloon application. In this method, a balloon filled with fluid or air in the stomach is placed under mild anesthesia with the help of an endoscope. This process takes 15-20 minutes. Thus, the food intake capacity of the stomach is reduced and rapid saturation is achieved.
With this method, patients can lose 7-8 pounds in a few months. However, this balloon can remain in the body for 6 months, a maximum of 1 year, and it is removed endoscopically in 5-6 minutes. Although the simple application and the absence of permanent changes in the body are the advantages of the method, the weight lost can be recovered if the patient does not change his lifestyle and continue his diet after the balloon is removed. However, within 6 months to 1 year of use, people are trained on how to eat by experimenting. This method, which has gradually lost its popularity today, is used as a preparation for basic morbidobesity surgery in patients who are too risky for surgery or super obese people. It may be ideal for people with a BMI of 30-40kg / m2.
Is Gastric Balloon A New Method?
The use of obesity as a non-surgical obesity treatment is a worldwide known and valid method. The idea of controlling obesity by giving a feeling of satiety with the help of a balloon that takes up space in the stomach was first developed in 1982. It has been proven by hundreds of studies that successful weight loss can be achieved with many different balloon types since then.
In a scientific congress held in Florida in 1987, many international experts came together and determined the basic design criteria for the ideal gastric balloon. In this way, the new generation gastric balloons produced have become an accepted treatment method in all Europe. Gastric balloon, which can be applied with an endoscopic method without the need for surgery, can be considered as an option to lose an average of 10-25 kg.
How to Attach a Gastric Balloon?
The gastric balloon is placed in the stomach with the help of an illuminated camera called an endoscope. This device has an average thickness of 0.8-12 mm and is flexible enough to easily pass through the esophagus. With the conscious sedation technique called sedoanalgesia applied by the anesthesiologist during the procedure, the patient is allowed to sleep completely for 10-15 minutes without stopping breathing. In other words, it is not possible to feel or remember anything during the procedure.
After the patient is put to sleep, a complete endoscopic examination is performed first. In other words, the entire upper digestive system from the esophagus to the duodenum is examined. If there is no reflux, ulcer, severe gastritis or suspicious lesion in the stomach, the endoscope is removed and the balloon is lowered into the stomach.
No discomfort occurs in the early period after the procedure. After a few hours, symptoms such as stomach cramps, nausea and vomiting may occur.
These side effects are due to the mass effect that the balloon creates in the stomach and usually lasts for a maximum of 3-4 days. In this process, the symptoms are alleviated by drugs taken either orally or intravenously. Very rarely, if the patient is not able to consume enough fluid, intravenous supplementation may be required.
In most patients, complaints disappear completely at the end of the first week. In very rare cases, the balloon may need to be removed early in cases where the symptoms do not alleviate and the balloon cannot be tolerated despite all treatments.


